Arguments against battery-electric vehicles (BEVs) usually end up with someone saying hydrogen is the “real” eco-friendly alternative to fossil fuel. But recently the EV naysayers have a new stick to beat BEVs with – synthetic fuels. For those who don’t like change, synthetic “e-fuels” are an even more obvious choice than hydrogen, because in theory they can be used with current internal combustion engines and refueling infrastructure. However, e-fuels are even less likely to solve the climate change problem than hydrogen. Here’s why.
Synthetic fuels are not a new discovery. But they have come back into the debate after Porsche head of research and development, Dr Michael Steiner, claimed recently that e-fuels could allow Porsche to continue to sell internal combustion engine cars alongside EVs, even after the UK bans fossil fuel engine sales in 2030. Porsche and Siemens have been developing synthetic fuels at a plant in Chile. In theory, synthetic fuels would reduce the CO2 emissions of internal combustion by around 85%, according to Porsche VP Dr Frank Walliser. That is obviously not zero, but it would clearly be a huge improvement over the current situation.

The energy inefficiency and slow development of synthetic fuels count them out as the main solution … [+]
GETTY
The argument certainly has some merits. The current refueling station infrastructure could be used with just a change of pump, and a much less onerous one than with hydrogen, which needs to be stored at 700 atmospheres so requires a completely different system. It is also a “killer feature” that these fuels are a drop-in replacement for current fossil fuels, meaning existing cars can use them without modification. Nobody would need to get a new car. This “business as usual” aspect appeals to those who dislike the lifestyle change that is entailed with owning a BEV (new type of car, charging at home, longer and more frequent recharging stops on a lengthy journey, and so on). Why bother with the upheaval if synthetic fuels solve the emissions problem without change?
Some have even argued that synthetic fuels will make BEVs the “Betamax” of environmental transport, referring to the format that lost out to VHS in the war of the 1970s and 1980s to be the dominant tape format for home video recording. Amusingly, Betamax was better technology, with a higher luminance resolution than VHS, so this metaphor already implies BEVs are an improvement over ICE. It lost the “videotape format war” because Sony made some questionable choices limiting its abilities (particularly tape length), and only changed this when it was too late. Betamax would probably have won otherwise.
This is clearly not going to happen with BEVs. The main vendors such as Tesla, Volkswagen, Renault and Kia-Hyundai are not limiting their cars’ abilities artificially. It is also worth noting that not even Steiner is expecting synthetic fuels to make BEVs irrelevant but allow Porsche to continue selling specialist vehicles like the 911 GT3. The timeframes of Porsche’s own initiatives do not fit mass adoption. The first trial output from the Chile facility will not be until 2022, and production is still only going to be 55 million liters by 2024, then around half a billion liters by 2026.
Putting this in perspective, the UK consumes 45-50 billion liters of fossil fuel a year, and in 2020, the USA consumed 123.49 billion gallons of finished motor gasoline in 2020, which is 467 billion liters. So Porsche’s Chile plant is going to supply scarcely 0.1% of what the US alone would require even by 2026. This is not the only company ramping up e-fuel production, but it is clearly a low-volume product aimed at specialist applications.
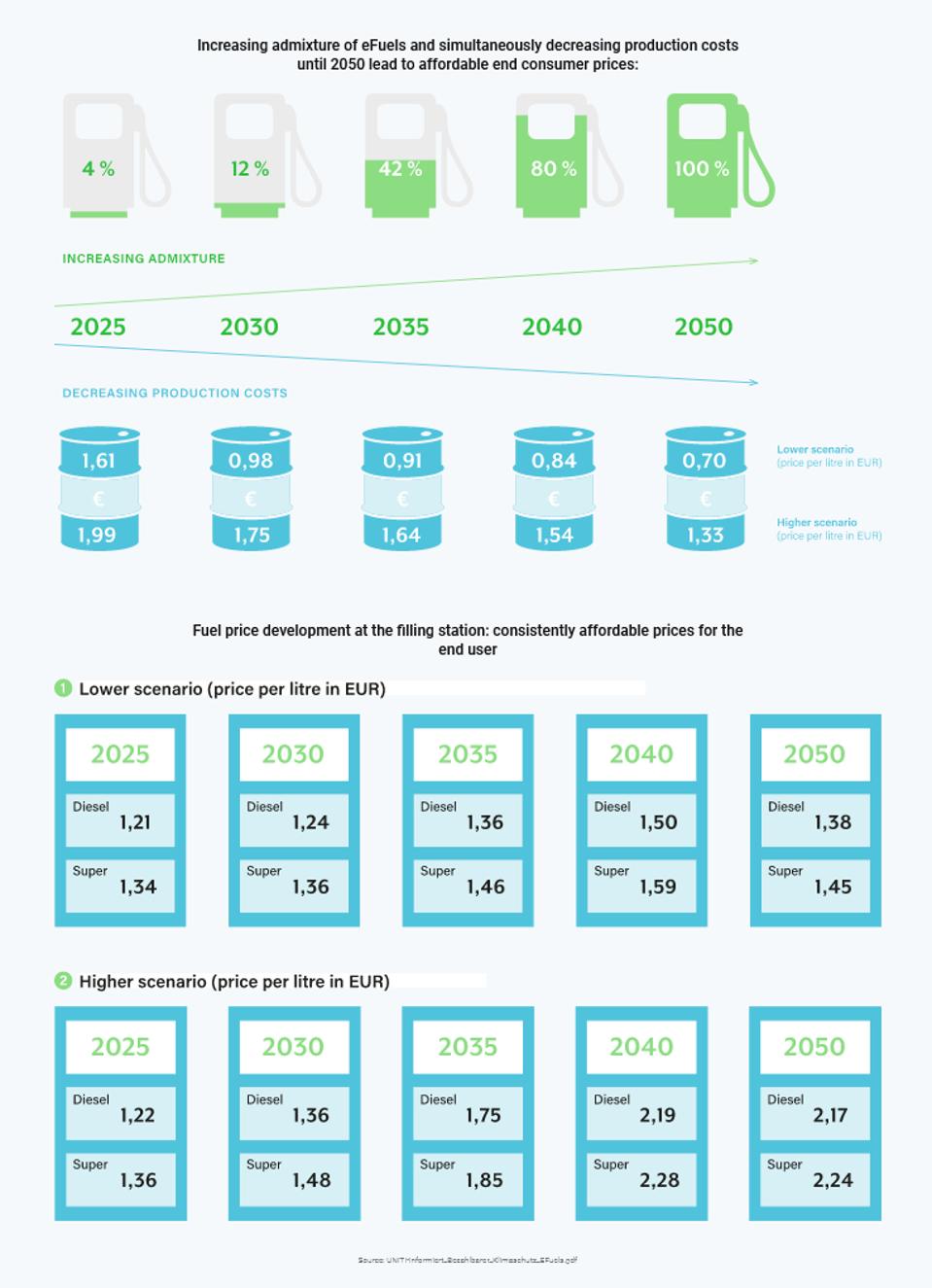
Even evangelists don’t expent 100% synthetic fuels to be available until 2050.
EFUELS ALLIANCE
The transition to synthetic fuel is not expected to be overnight, though. The efuel Alliance sees gradually increasing synthetic admixture to conventional fossil fuels rather than an immediate swap. This would alleviate the slow initial supply, but the expectation is for just 4% admixture by 2025, 12% by 2030, and only 100% by 2050. That is just too late to solve the current climate crisis. The claims for pricing are ridiculous too, with the eFuel Alliance expecting synthetic fuel to cost between 1.38 and 2.24 Euros by 2050 ($1.63 to $2.64). Bosch has gone even further, claiming synthetic fuel would be 1.20 Euros ($1.41 ) by 2030. More realistic estimates put the cost at more like 3 or 4 Euros a liter ($3.54 to $4.72) by 2030, which equates to over $13 a US gallon. That is quite a bit more than the current US average of $3.20 a gallon, and highly likely to result in car owners looking to ditch their internal combustion cars, or stick with regular gasoline if they are allowed.
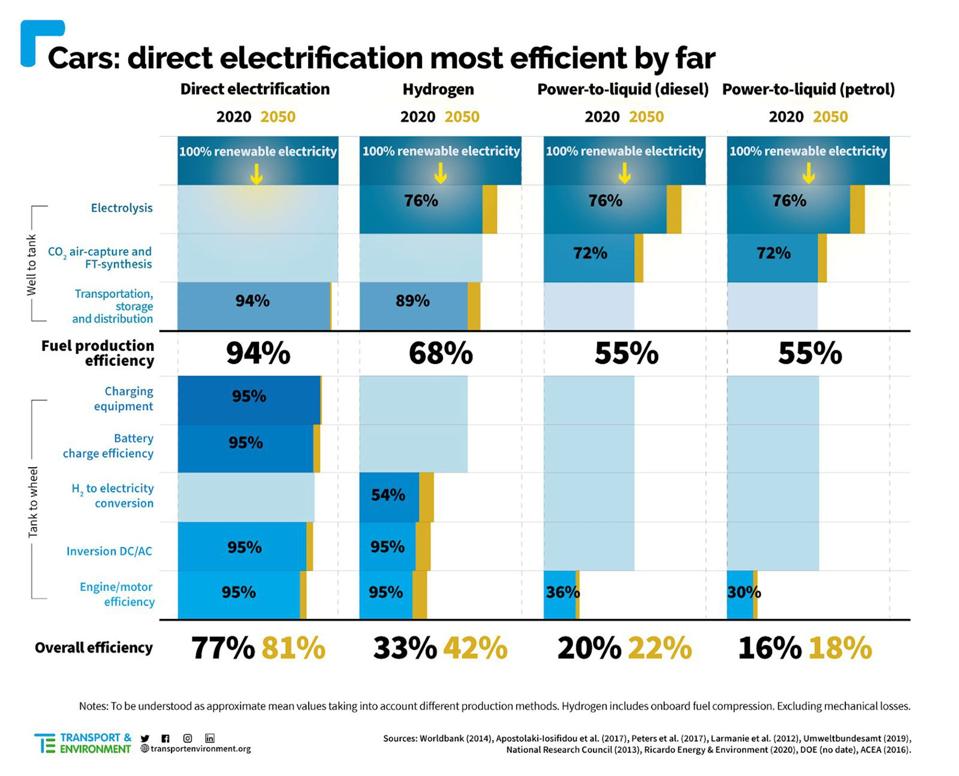
The elephant in the room comes from how synthetic fuels are made. They are produced by combining CO2 with hydrogen, and this raw material is then used to manufacture the sub-type – gasoline/petrol or diesel. Not only does this process involve lots of stages, each of which adds cost and consumes energy, the key element here is hydrogen, which leads to a similar set of questions about energy efficiency as hydrogen fuel cells. In fact, the situation is even worse for synthetic fuel. According to Transport & Environment, hydrogen fuel cells are currently 2.3 times less energy efficient than batteries, with the deficit dropping to 2 times less efficient by 2050. Synthetic fuels are less efficient still, with the estimate being about 4 times worse than batteries and very little improvement by 2050. In other words, powering the current car fleet with synthetic fuels instead of batteries will require four times as much electricity generation, which seems completely impractical. If just 10% of the UK’s cars, vans and small trucks used e-fuels it would require three times as much renewable electricity as batteries. It is also therefore entirely impossible that synthetic fuel will be cheaper than using electricity to charge batteries.
Synthetic fuels (“power-to-liquid”) are even less efficient than hydrogen fuel cells for powering … [+]
TRANSPORT & ENVIRONMENT
This is, of course, assuming the hydrogen is produced with renewable energy, and only 1% of current hydrogen is generated in this way. The rest of it comes from various types of fossil fuel-based processes, which still produce emissions to a greater or lesser extent (grey or blue hydrogen). Right now, hydrogen is not really a green fuel at all, it is the oil and gas industry trying to remain relevant in a rapidly changing world. Grey and blue hydrogen is cheaper than producing it from water and electricity, but no answer to the environmental problems the planet now faces.
Putting all these together, synthetic fuel will be too little, too late, and for too much money per mile. At best, e-fuels will delivery an 85% reduction in vehicle CO2 by 2050. In contrast, in countries with a high deployment of renewable energy such as the UK, BEVs can deliver 100% reduction in vehicle CO2 emissions right now. Which one do you think is mostly likely to save the planet from the climate change crisis?